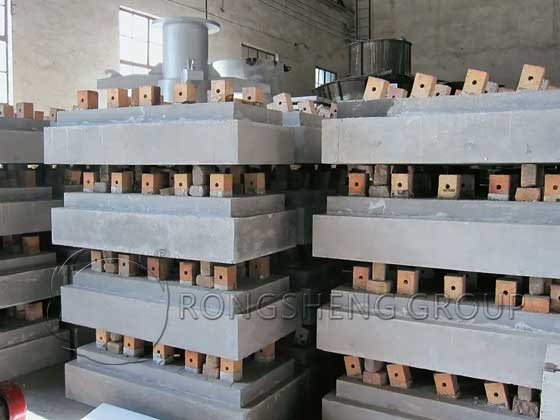
Rongsheng Refractory Materials Manufacturer specializes in the research, development, and production of shaped and unshaped refractories, providing comprehensive life-cycle services for thermal kiln linings, including refractory material configuration, furnace lining optimization, engineering construction, and technical services. Rongsheng also boasts an environmentally friendly, fully automated production line for unshaped refractories, professionally producing various types. Among unshaped refractories, abrasion resistant refractory, those with common refractory and wear-resistant properties include the following:
Ordinary Wear-Resistant Plastic
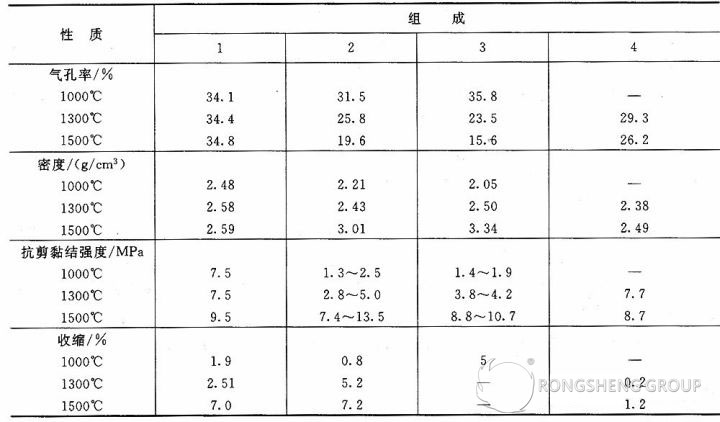
Ordinary wear-resistant plastic is a high-alumina, corundum-based granular product. Compared with traditional refractory plastics, it has excellent properties such as easy construction, high efficiency, good molding, and high strength. abrasion resistant refractory. This material is composed of adhesive, refractory aggregate, and hardening accelerator. Adding a certain proportion of PA adhesive forms a plastic refractory mortar, facilitating construction in various complex areas. It is an air-hardening material with low-temperature hardening properties, ensuring the wear resistance required for circulating fluidized bed boilers. However, its wear resistance is relatively poor.
- 1) Application Method: Use a forced mixer to stir the material, adding the accelerator evenly during stirring. After dry stirring for 1 minute, add 4-5% of the adhesive and stir for another 3 minutes. Once the material reaches a certain plasticity, it can be unloaded and used.
- 2) Applicable Areas: Suitable for high-temperature areas with low friction, such as the boiler bottom air chamber, primary air duct, return riser (material leg), return feeder, return pipe, tail flue furnace wall, slag cooler, and filling of various furnace doors in the tail flue. 3) Storage method. Generally, store in a cool, dark place. Shelf life is about 2 to 3 months.

Wear-Resistant Refractory Plastic
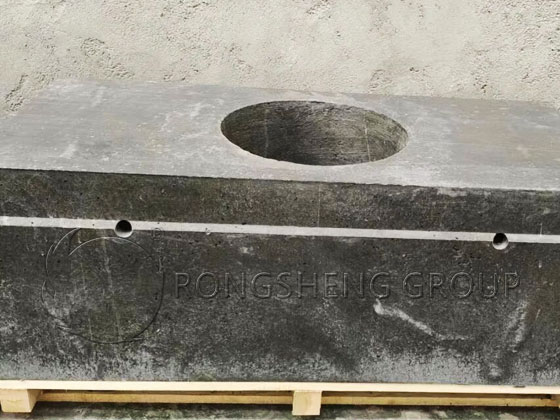
Abrasion-resistant refractory plastics are made from high-alumina bauxite clinker, corundum, mullite, and silicon carbide as aggregates. They possess excellent wear resistance, strong adhesion, and a high service temperature. Formulated with different binders and additives, they are refractory materials with high strength and wear resistance. They offer advantages such as easy construction, good plasticity, and excellent wear resistance. The applied wear-resistant layer has high strength and wear resistance, fully meeting the performance requirements of wear-resistant refractory materials for boilers.
- 1) Application Method: The materials and binder are mixed evenly with phosphoric acid before use. Construction is typically carried out using a ramming process.
- 2) Applicable Areas
- Suitable for construction in thin-thickness areas such as furnace water-cooled walls, mainly used in the dense phase zone of the furnace and in steam-cooled and water-cooled cyclone separators. In this area, the wear-resistant refractory material is designed as a single-layer rammed structure, fixed with wear-resistant pins, and its design thickness is relatively thin, directly applied to the construction surface.
- In the repair of circulating fluidized bed cyclone separators, its superior bonding properties allow for the repair of any irregular wear areas without the need for steel templates or molds. Ignition can be performed immediately after construction, requiring no special curing, thus shortening the construction cycle and saving costs.
- 3) Storage method. Avoid open-air storage and direct sunlight. Store in a cool, damp place in summer and protect from freezing in winter.
Corundum Wear-Resistant Refractory Plastic
This material belongs to the field of high-temperature wear-resistant refractory materials. The raw materials consist of high-alumina homogeneous material, alumina micropowder, silica micropowder, clay, phosphoric acid, aluminum dihydrogen phosphate solution, and pure calcium aluminate cement. Its key feature is the use of low-water-absorption, low-porosity, and highly uniform synthetic homogeneous materials to replace traditional high-water-absorption, high-porosity, and poorly uniform sintered bauxite clinker natural raw materials or corundum composite raw material systems, producing a homogeneous, high-strength, wear-resistant corundum plastic.
- 1) Application Method: This material is applied using a tamping process, suitable for thin-thickness applications such as furnace water-cooled walls. The resulting wear-resistant layer exhibits high strength and wear resistance. Unlike castables, this plastic does not require molds and can be applied directly using a smearing and tamping method. The refractory plastic material has good workability, high strength, and good wear resistance, resulting in optimal performance in the field. It helps extend the service life of furnace linings and improve the utilization efficiency of high-temperature kilns.
- 2) Applicable Areas. It is mainly used in the dense phase zone of the furnace and in steam-cooled/water-cooled/insulated cyclone separators. The wear-resistant refractory material in this area is designed as a single-layer rammed structure and fixed with wear-resistant pins. Its thickness varies, generally 40-60mm (steam-cooled/water-cooled) and 320-350mm (insulated), and it can be directly laid on the construction surface.

Silicon Carbide Corundum Wear-Resistant Refractory Plastic
Silicon carbide corundum wear-resistant refractory plastic is a high-grade refractory material. It possesses excellent wear resistance, strong adhesion, and a high service temperature. It is also renowned for its simple construction process, short construction period, and the superior characteristic of not requiring furnace drying after construction. In practice, its service life is significantly longer than other wear-resistant refractory materials, and it is widely used in industries such as power, metallurgy, steel, and ceramics.
- 1) Application Method: This material is applied using a smearing and tamping method. Before application, rigid anchor pins should be fixed to the required locations, with a mesh spacing of approximately 120-150mm (maximum not exceeding 200mm). During application, the plastic is laid evenly on the required areas. The thickness of the smear can be determined according to the design requirements of different furnace types.
- 2) Applicable Areas: Silicon carbide wear-resistant refractory plastic can be widely used in cyclone separators, thermal radiation materials, and other applications where refractory materials are used. It possesses superior adhesive properties, allowing for easy application and application to any irregular, worn areas, significantly reducing wear. No steel templates or molds are required; it can be ignited immediately after application without special curing, thus shortening the construction cycle and saving costs.
- 3) Storage Method. Avoid open-air storage and direct sunlight. In summer, store in a cool, damp place; in winter, protect from freezing. The shelf life of the plastic is generally one year, and the accelerator should be replaced after 4-6 months of unused use (if used after one year of storage, the material must be re-cured).
High-Strength Wear-Resistant Refractory Plastics
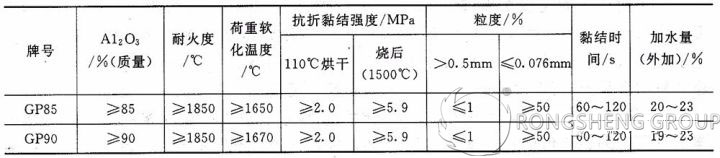
Rongsheng’s high-strength wear-resistant refractory plastics belong to the high-strength wear-resistant series of refractory plastics. Their materials include high-alumina, corundum, silicon carbide, chromium, and zircon.
High-strength wear-resistant refractory plastics possess strong plasticity and wear resistance. They can be tamped into any shape using the tamping method, making them a quick-repairing material for kiln linings.
High-strength wear-resistant refractory plastics are refractory plastics composed of the above-mentioned materials as the main raw materials, with the addition of binders and additives (shrinkage inhibitors, preservatives, and antifreeze agents).
Commonly used castables include: corundum wear-resistant refractory castables, wear-resistant refractory plastics, non-stick alumina castables, low-cement refractory castables, adjustable-mouth castables, high-strength impermeable low-cement castables, lightweight refractory insulating castables, and steel fiber refractory castables.
Applications of High-Strength Wear-Resistant Plastics:
- In the power generation industry: coal unloading trenches, coal hoppers, coal storage bins, dry coal grids, tippers, slag removers, water treatment, etc.
- In the chemical industry: corrosion-resistant flooring, pump foundations, etc.
- In the coal industry: wear-resistant linings for grinding bins, medium tanks, scraper conveyors, bucket elevators, chutes, underscreen hoppers, etc.; in the steel industry: blast furnace mixing bins, sintering bins, feeders, pelletizing machines, etc.